Peanut butter nutrition labels provide key information about what’s in your peanut butter. Peanut butter is a beloved food in many homes, famous for its delicious taste and health benefits.
It’s not just for spreading on toast; you can blend it in smoothies or use it in recipes. But to eat smart, it’s important to understand what’s written on those peanut butter jars. Let’s explore the nutrition labels of peanut butter to help you make better food choices.
Understanding Peanut Butter Nutrition Labels
Peanut butter is a favorite food for many, and it’s good for you too! Let’s look at what you find on a peanut butter nutrition label:
Nutritional Facts

- Calories: Each serving, about two tablespoons, has 180-200 calories. It’s a bit high in calories, but it’s also filling.
- Total Fat: A serving has about 16-18 grams of fat. Most of this fat is good for your heart – they are called monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
- Saturated Fat: Each serving has about 3-3.5 grams of saturated fat. This is the kind of fat you don’t want too much of.
- Trans Fat: Good peanut butter has no trans fat, which is great because trans fat is not good for your health.
- Cholesterol: Peanut butter doesn’t have cholesterol, which is good news for your heart.
- Sodium: The amount of salt in peanut butter can change. Natural or unsweetened kinds usually have less salt.
Protein and Carbohydrates
- Protein: Peanut butter is a good way to get protein. One serving has about 7-8 grams of it.
- Carbohydrates: A serving has about 6-8 grams of carbs. This includes 2-3 grams of fiber (good for your tummy) and 1-2 grams of sugar.
Just remember to check the label and eat it in moderation, as it’s high in calories.
Vitamins and Minerals

Peanut butter is a good source of several vitamins and minerals, including:
- Vitamin E
- Magnesium
- Phosphorus
- Zinc
- Niacin (Vitamin B3)
Ingredient List
The ingredient list on a peanut butter jar can reveal a lot about its quality and nutritional value. Ideally, it should be short and simple.
Types of Ingredients
- Peanuts: The primary ingredient, accounting for over 90% of the content in natural peanut butter.
- Added Sugars: Some brands add sugar for flavor. Opting for a brand with little to no added sugar is healthier.
- Salt: Used for flavor enhancement.
- Hydrogenated Oils: Often added to prevent oil separation. Natural peanut butter, which requires stirring, typically doesn’t contain these oils.
Allergen Information
Peanut butter is a common allergen. Labels usually include an allergen statement, which is especially important for those with peanut allergies.
Health Considerations of Peanut Butter
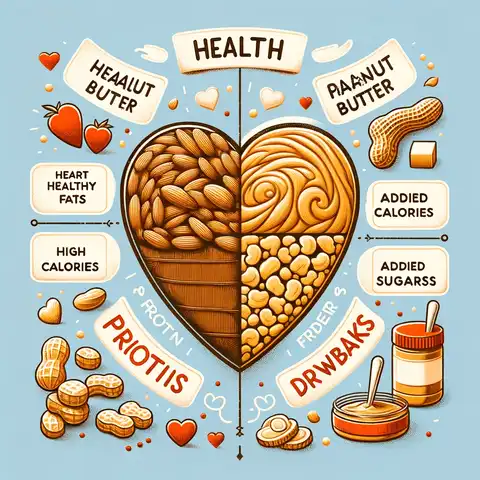
Peanut butter is not just tasty; it’s also good for you in some ways. Let’s check them out:
Benefits
- Heart-Healthy Fats: Some fats in peanut butter are good for your heart.
- Protein: Peanut butter has protein. This helps make your muscles strong and fixes them when needed.
- Fiber: There’s also fiber in peanut butter. This helps your tummy work well.
Drawbacks
- Calories: Peanut butter has a lot of calories. In just two tablespoons, there are about 180-200 calories.
- Added Sugars and Fats: Some peanut butter, especially those that are not natural, puts in extra sugars and not-so-good fats. These aren’t as healthy.
Peanut butter can be really good for you, but it’s best to eat it smartly. Look for kinds without too much sugar and bad fats, and remember, don’t eat too much because it’s got a lot of calories.
Types of Peanut Butter: Natural vs. Regular
Peanut butter comes in two main kinds: Natural and Regular. Let’s look at what makes them different:
Natural Peanut Butter
- Made Mostly of Peanuts: This is almost all peanuts, over 90%!
- Not Much Processing: It keeps most of the good stuff from peanuts because it’s not often processed.
- A Little Salt, No Sugar: It might have some salt but no added sugar or stuff to keep it fresh.
- Oil Separation: You’ll see the oil on top because it’s natural. Just stir it before you use it.
- Healthier Option: It’s good for you because it doesn’t have added sugar or bad fats.
Regular Peanut Butter
- Extra Ingredients: This kind has more than just peanuts. It often has added sugar, oils to keep it from separating, and more salt.
- Smooth and Creamy: Because of the added oils, it doesn’t separate and is creamy.
- Sweeter Taste: It tastes more precious and the same every time because of the added sugars and flavors.
- Lasts Longer: It stays good longer because of the extras added to it.
- More Calories and Fat: It can have more calories and not-so-good fats. If you’re watching your salt, this kind has more.
Choosing Between Natural and Regular
- Dietary Needs and Preferences: Pick natural peanut butter for less sugar and a simple taste. Choose regular if you want something easy to spread and sweeter.
- How You Use It: Use natural peanut butter in recipes that need real peanut flavor or if you’re avoiding sugar. Regular peanut butter is handy for everyday use.
Both kinds give you the goodness of peanuts, but natural peanut butter is simpler and healthier. Regular peanut butter is more about easy use and a consistent sweet taste.
Popular peanut butter food label brands and types
Reveals the variety of nutritional content and ingredients across various brands and types.
Here’s what you might find on the labels of some popular peanut butter brands and types:
Skippy Peanut Butter food label

- Calories: Around 190-200 per serving (2 tablespoons).
- Fat: Approximately 16-17 grams, with saturated fat usually around 3 grams.
- Sugar: About 3 grams of added sugars.
- Protein: Roughly 7 grams per serving.
Jif Peanut Butter food label

- Calories: Typically 190 calories per serving.
- Fat: Around 16 grams, including 2.5-3 grams of saturated fat.
- Sugar: Contains added sugars, around 3 grams.
- Protein: About 7 grams per serving.
Reese’s Peanut Butter food label

- Calories: Slightly higher due to added sugar, around 200 calories.
- Fat: About 16 grams, with saturated fat near 3 grams.
- Sugar: Higher sugar content, approximately 4-5 grams.
- Protein: Similar to other brands, around 7 grams.
Natural Peanut Butter food label

- Calories: About 180-200 calories.
- Fat: Higher in healthy fats, around 16-18 grams.
- Sugar: No added sugars, natural sugars around 1-2 grams.
- Protein: Around 8 grams per serving.
Peter Pan Peanut Butter food label

- Calories: Approximately 190-200 calories.
- Fat: About 16 grams, with 3 grams of saturated fat.
- Sugar: 3 grams of added sugars.
- Protein: 7-8 grams per serving.
Kraft Peanut Butter food label

- Calories: Around 190 calories per serving.
- Fat: Typically 16 grams, including saturated fat.
- Sugar: Added sugars around 3 grams.
- Protein: About 7 grams per serving.
Smucker’s Natural Peanut Butter food label

- Calories: Around 180-200 calories.
- Fat: Higher in monounsaturated fats, around 16 grams.
- Sugar: No added sugars.
- Protein: Approximately 8 grams per serving.
Reduced Fat Peanut Butter food label

- Calories: Slightly lower, around 180 calories.
- Fat: Reduced fat content, about 12 grams.
- Sugar: Can vary, sometimes higher to compensate for flavor.
- Protein: Around 7 grams per serving.
Häagen-Dazs Chocolate Peanut Butter (Ice Cream)

- Calories: Significantly higher due to being ice cream, around 300-350 calories per serving.
- Fat: High-fat content, including saturated fat.
- Sugar: High sugar content.
- Protein: Lower than peanut butter, around 5-6 grams per serving.
The nutritional content can vary slightly based on the specific product and flavor.
In conclusion, peanut butter is great when you choose a healthy kind and eat it in the right amounts. Just remember to check those labels and enjoy it as part of a balanced diet.




